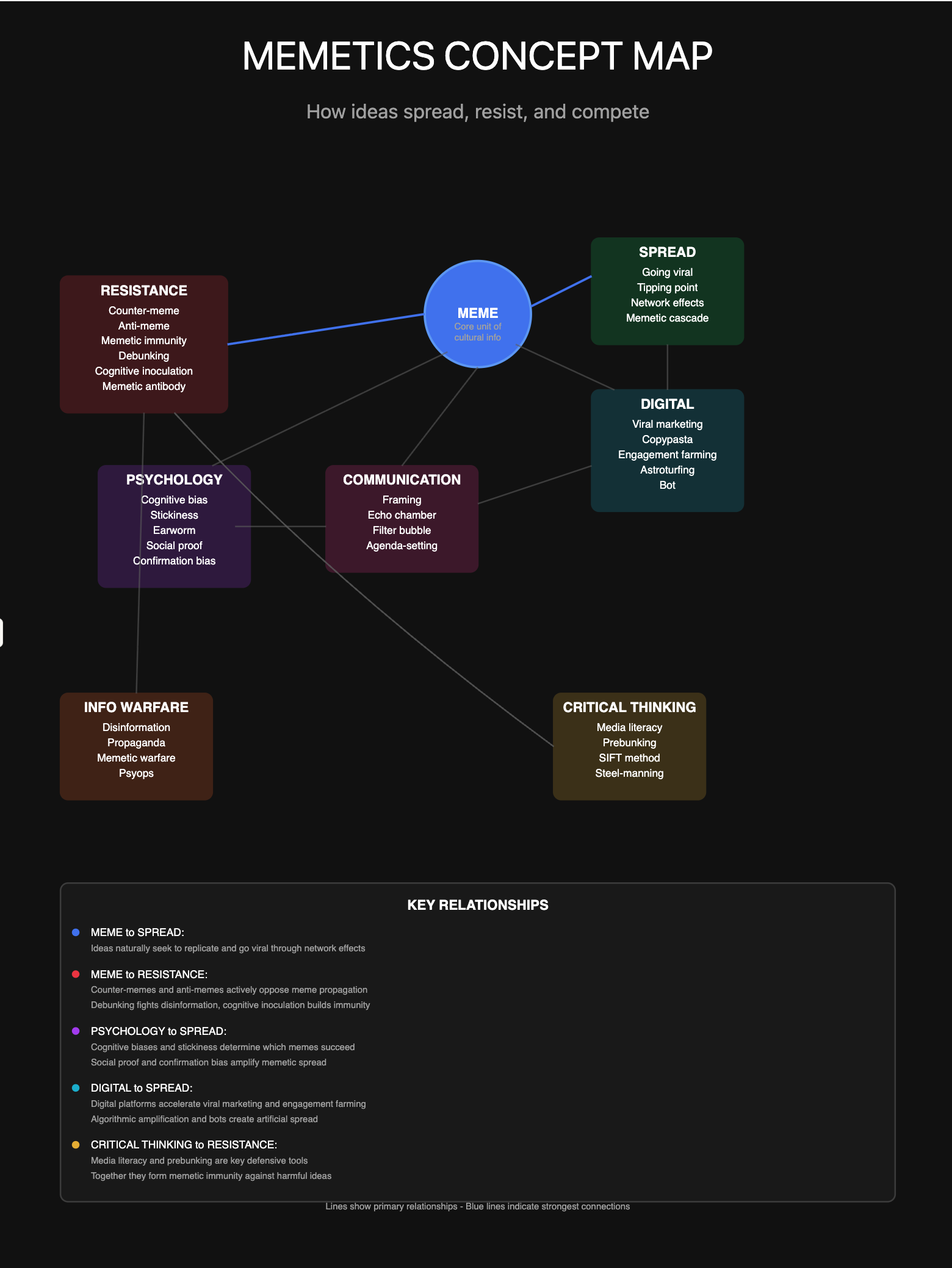
Memetic Lexicon
Memetic behavior does not share language across sectors but boy does it have presence. Resistance + Critical thinking boxes are defense the others offense to move men to action
Core Memetics Terms
Meme - A unit of cultural information that spreads from person to person (coined by Richard Dawkins, 1976) Memeplex - A group of memes that work together and reinforce each other (like a religion or political ideology) Memetic engineering - Deliberately designing ideas to spread effectively Memetic fitness - How well-suited a meme is to replicate and spread Virality - The capacity for rapid, exponential spreading Transmission vector - The medium through which a meme spreads (social media, word-of-mouth, etc.) Replicator - Any information pattern that copies itself (memes, genes, etc.)
Resistance & Opposition Terms
Counter-meme - A meme designed to fight another meme Anti-meme - Information that resists being known or remembered Memetic immunity - Resistance to accepting certain memes Cognitive inoculation - Pre-exposing people to weak arguments to build resistance Debunking - Actively refuting false memes Fact-checking - Verifying or disproving memetic claims Memetic antibody - Ideas that neutralize harmful memes Steelmanning - Presenting the strongest version of an opposing idea (opposite of strawmanning)
Spread Dynamics
Going viral - Achieving exponential spread Memetic cascade - Chain reaction of meme transmission Tipping point - Critical mass where a meme becomes self-sustaining Network effects - When a meme becomes more valuable as more people adopt it Memetic drift - Gradual changes in a meme as it spreads Mutation - Variations that emerge as memes are copied Selection pressure - Environmental factors favoring certain meme variants Horizontal transmission - Spreading between peers Vertical transmission - Passing from generation to generation
Psychology & Cognitive Science Terms
Cognitive bias - Mental shortcuts that affect which memes we accept Confirmation bias - Preferring information that confirms existing beliefs Availability heuristic - Overweighting easily recalled information Anchoring - First information received disproportionately influences thinking Salience - How noticeable or attention-grabbing something is Stickiness - How memorable an idea is (from “Made to Stick”) Earworm - A catchy tune that gets stuck in your head Thought-terminating cliché - A phrase that shuts down critical thinking Semantic stop sign - A word/phrase where people stop asking “why?” Applause lights - Statements designed to trigger automatic approval Curiosity gap - Creating desire to know missing information (clickbait uses this) Narrative transportation - Being absorbed into a story, making it persuasive Social proof - Following what others do/believe
Information Warfare & Propaganda
Disinformation - Deliberately false information spread to deceive Misinformation - False information spread without malicious intent Malinformation - True information used to cause harm Propaganda - Information designed to promote a particular viewpoint Astroturfing - Fake grassroots movements Gaslighting - Making people doubt their own perceptions Narrative warfare - Competing to control the dominant story Memetic warfare - Using ideas as weapons Info-ops (Information operations) - Military/intelligence term for influence campaigns Psyops (Psychological operations) - Military psychological manipulation Active measures - Soviet term for influence operations Dezinformatsiya - Russian term for disinformation
Communication Studies Terms
Framing - How information is presented affects interpretation Priming - Earlier information influences later interpretation Agenda-setting - Media determining what topics people think about Spiral of silence - People suppress minority opinions, making them seem rarer Echo chamber - Environment where beliefs are amplified and reinforced Filter bubble - Personalized information limiting exposure to different views Epistemic bubble - Lacking exposure to other viewpoints Two-step flow - Ideas spread from media to opinion leaders to general public Diffusion of innovations - How new ideas spread through populations (Rogers’ theory) Adopter categories - Innovators, early adopters, early majority, late majority, laggards
Marketing & Advertising
Viral marketing - Marketing designed to spread organically Influencer - Person with power to affect others’ behavior Brand evangelist - Customer who voluntarily promotes a brand Word-of-mouth (WOM) - Organic person-to-person recommendation Buzz marketing - Generating excitement and conversation Guerrilla marketing - Unconventional, attention-grabbing tactics Astroturfing - Fake grassroots enthusiasm Native advertising - Ads designed to look like regular content Engagement - How much people interact with content Reach - How many people are exposed Impressions - Number of times content is displayed Conversion - When someone takes desired action
Internet & Digital Culture
Copypasta - Text repeatedly copied and pasted Shitposting - Deliberately low-quality or ironic content Ratio - When a reply gets more engagement than the original post Quote-tweet dunk - Mocking someone by sharing their post with commentary Dogpiling - Mass coordinated criticism of someone Brigading - Coordinated group invasion of a space Astroturfing - Coordinated fake grassroots activity Sockpuppet - Fake online identity Bot - Automated account spreading content Troll - Person deliberately provoking reactions Ragebait - Content designed to anger people into engaging Engagement farming - Creating content solely for metricsAlgorithmic amplification - Platform algorithms boosting certain content
Resistance & Critical Thinking
Media literacy - Ability to critically analyze information Digital literacy - Understanding how digital information works Prebunking - Preemptively debunking before exposure Lateral reading - Verifying by checking multiple sources SIFT method - Stop, Investigate source, Find better coverage, Trace claims Steel-manning - Addressing the strongest version of an argument Socratic questioning - Using questions to examine ideas critically Epistemic humility - Acknowledging limits of one’s knowledge Intellectual honesty - Fairly representing evidence and arguments Bad faith - Arguing dishonestly or without genuine belief Good faith - Arguing honestly with genuine intentions
SCP Foundation & Fiction Terms
Memetic hazard - Information that harms those who perceive it Cognitohazard - Information dangerous to know Infohazard - Information that causes harm when known Antimemetic - Self-censoring, unmemorable information Memetic kill agent - Information that kills or incapacitates Memetic vaccine - Protective exposure to weakened hazard Class-A amnestic - Fictional memory-erasing drug Containment protocol - Procedures to prevent spread
Academic Fields
Memetics - Study of meme evolution and spread Cultural evolution - How cultures change through information transmission Epidemiology - Study of disease spread (applied to ideas) Diffusion studies - How innovations spread through societies Social contagion - Spread of behaviors/emotions through populations Information theory - Mathematical study of information transmission Semiotics - Study of signs and symbols Rhetoric - Art of persuasive communication Cognitive science - Study of mind and intelligence Behavioral economics - How psychology affects economic decisions
Related Biological Metaphors
Viral - Spreading like a virus Contagion - Disease-like transmission Vector - Carrier of infection/informatio Host - Person carrying and spreading a meme Reservoir - Source maintaining meme existence Carrier - Person transmitting without symptoms/belief Incubation period - Time before meme manifests/spreads Outbreak - Sudden rapid spread Epidemic - Widespread occurrence in a population Pandemic - Global spread Herd immunity - Enough resistance to prevent spread Pathogen - Disease-causing agent (harmful meme) Symbiosis - Mutually beneficial meme relationship Parasitism - Meme benefiting at host’s expense
Counter-meme - The most common term. This is a meme specifically designed to combat or neutralize another meme. For example, fact-checking content that debunks misinformation, or a counter-narrative that undermines a viral idea.
Meme antibody - Sometimes used metaphorically, drawing on the biological analogy where antibodies neutralize pathogens.
Debunk or rebuttal - In practical contexts, simply the counter-information that stops a false meme from spreading.
Inoculation - From “inoculation theory,” this refers to pre-emptively exposing people to weakened versions of bad arguments so they develop resistance to persuasive misinformation.
Memetic hazard countermeasure - Used in fiction (like SCP Foundation) for specific protocols to stop harmful ideas.
Unlike “anti-meme” (which describes something inherently unmemorable), a counter-meme is still a meme itself—it spreads easily, but its purpose is to neutralize another meme. Think of it like a viral video debunking a conspiracy theory: it uses memetic properties (catchiness, shareability) to fight another meme.